Openning the gate
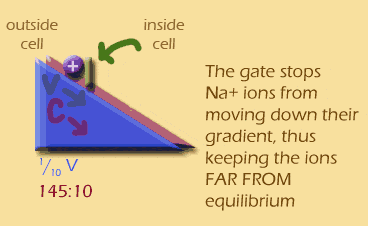
And when you open the gate? Sodium ions rush into the cell, essentially heading down two gradients at once.
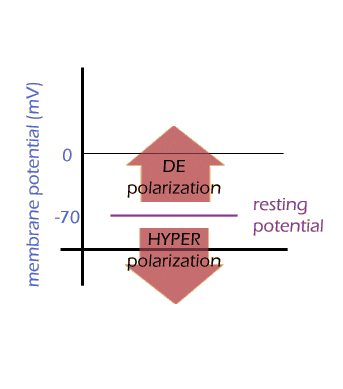 That creates a drastic and rapid change in the membrane's potential, called "depolarisation" -- because the charges are becoming less polarised, or separated.
That creates a drastic and rapid change in the membrane's potential, called "depolarisation" -- because the charges are becoming less polarised, or separated.
(It's a little confusing to talk about the change in membrane potential. In fact any movement towards a "more positive" membrane potential is called "depolarisation", even if the resulting potential is still negative. And any movement toward a more negative potential is called "hyperpolarisation". This only makes sense because the resting potential is already negative.)
Copyright University of Maryland, 2007
You may link to this site for educational purposes.
Please do not copy without permission
requests/questions/feedback email: mathbench@umd.edu