And what you've all been waiting for
Using the equation governing the flow of sugar across a membrane:
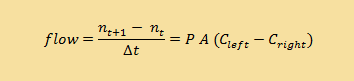
and given that
The area of the membrane between the two solutions is 2 cm2
The concentration of the solution on the left side of the membrane = 0.4 M
The concentration of the solution on the right side of the membrane = 0.1 M
P= 0.02 cm/sec
What is the rate of diffusion (flow rate) across the membrane for the following concentrations? This kind of problem requires straightforward substitution...
0.02cm/sec x 2 cm2 x (0.4 M sugar - 0.1 M sugar)
= 0.012 moles/second
The flux (flow rate divided by the area) would therefore be 0.012 / 2 = 0.006 mol cm -2 s -1
What would happen if we doubled the permeability constant?
What if we doubled the area of the membrane?
What if we doubled the concentration on the left?
Copyright University of Maryland, 2007
You may link to this site for educational purposes.
Please do not copy without permission
requests/questions/feedback email: mathbench@umd.edu